- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录62 > MLX90215EVA-AAA-106-BU (Melexis Technologies NV)IC SENSOR PROG LINEAR HALL 4SIP
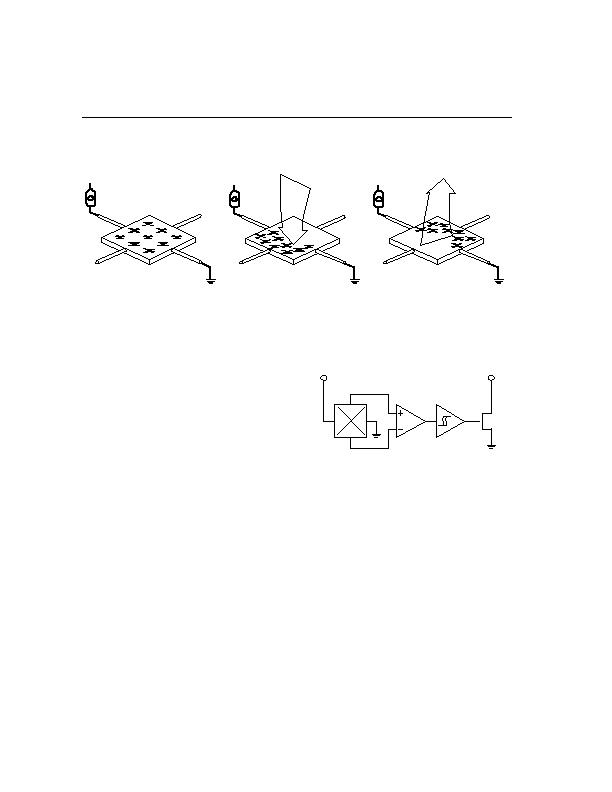
The Hall-Effect
The Hall-Effect principle is named for physicist Edwin Hall. In 1879 he discovered that when a conductor or
semiconductor with current flowing in one direction was introduced perpendicular to a magnetic field a voltage
could be measured at right angles to the current path.
The Hall voltage can be calculated fromV
Hall
= 肂 where:
V
Hall
= emf in volts
?=
sensitivity in Volts/Gauss
B =
applied field in Gauss
I =
bias current
The initial use of this discovery was for the classification
of chemical samples. The development of indium arsenide
semiconductor compounds in the 1950's led to the first
useful Hall effect magnetic instruments. Hall effect sen-
sors allowed the measurement of DC or static magnetic
fields with requiring motion of the sensor. In the 1960's
the popularization of silicon semiconductors led to the
first combinations of Hall elements and integrated ampli-
fiers. This resulted in the now classic digital output Hall
switch. (right)
The continuing evolution of Hall transducers technology saw a progression from single element devices to dual
orthogonally arranged elements. This was done to minimize offsets at the Hall voltage terminals. The next pro-
gression brought on the quadratic of 4 element transducers. These used 4 elements orthogonally arranged in a
bridge configuration. All of these silicon sensors were built from bipolar junction semiconductor processes. A
switch to CMOS processes allowed the implementation of chopper stabilization to the amplifier portion of the
circuit. This helped reduce errors by reducing the input offset errors at the op amp. All errors in the circuit non
chopper stabilized circuit result in errors of switch point for the digital or offset and gain errors in the linear out-
put sensors. The current generation of CMOS Hall sensors also include, a scheme that actively switched the
direction of current through the Hall elements. This scheme eliminates the offset errors typical of semiconduc-
tor Hall elements. It also actively compensates for temperature and strain induced offset errors. The overall
effect of active plate switching and chopper stabilization yields Hall-Effect sensors with an order of magnitude
improvement in drift of switch points or gain and offset errors.
Melexis uses the CMOS process exclusively, for best performance and smallest chip size. The developments to
Hall-Effect sensor technology can be credited mostly to the integration of sophisticated signal conditioning cir-
cuits to the Hall IC. Recently Melexis introduced the worlds first programmable linear Hall IC, which offered
a glimpse of future technology. Future sensors will programmable and have integrated microcontroller cores to
make an even
smarter
sensor.
V
H
V
H
No Magnetic
Field
V
H
V
H
South
Magnetic Field
V
H
V
H
North Magnetic
Field
V
DD
Output
GND
Digital Hall Effect Switch
V +
Differential
Amplifier
Schmidt
Trigger
Hall
Plate
Output
GND
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
MX887DHTTR
MICROPOWER HALL-EFFECT SWITCH
MX887PHTTR
IC HALL EFFECT SW UPWR TSOT23-3
OMH3040S
SENSOR HALLOGIC HALL EFFECT
OPB122B
SWITCH SLOTTED OPTIC PHOTOLOGIC
OPB200
SENSR OPTO SLOT 5.1MM TRANS THRU
OPB202
SWITCH SLOTTED OPTICAL
OPB483T11
SWITCH PHOTOLOGIC SLOTTD OPTICAL
OPB660N
SENS OPTO SLOT 3.18MM TRAS W/RES
相关代理商/技术参数
MLX90215LVA
制造商:未知厂家 制造商全称:未知厂家 功能描述:Precision Programmable Linear Hall Effect Sensor
MLX90215LVA-AAA-111-BA
制造商:Melexis Semiconductors 功能描述:IC HALL EFFECT SENSOR PREC 4SIP
MLX90215LVA-AAA-111-BU
功能描述:IC SENSOR PROG LINEAR HALL 4SIP RoHS:是 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR
MLX90215LVA-BC03
功能描述:IC SENSOR LIN HALL 10MV/MT 2.5V RoHS:是 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR
MLX90215LVA-CC03
功能描述:IC SENSOR LIN HALL 20MV/MT 2.5V RoHS:否 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR
MLX90215LVA-GC03
功能描述:IC SENSOR LIN HALL 50MV/MT 2.5V RoHS:否 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR
MLX90215LVA-LA03
功能描述:IC SENSOR LIN HALL 100MV/MT 1V RoHS:否 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR
MLX90215LVA-LC03
功能描述:IC SENSOR LIN HALL 100MV/MT 2.5V RoHS:否 类别:传感器,转换器 >> 磁性 - 霍尔效应,数字式开关,线性,罗盘 (IC) 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 传感范围:20mT ~ 80mT 类型:旋转 电源电压:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:15mA 电流 - 输出(最大):- 输出类型:数字式,PWM,8.5 位串行 特点:可编程 工作温度:-40°C ~ 150°C 封装/外壳:20-SSOP(0.209",5.30mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:20-SSOP 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:AS5132-HSST-500DKR